Earth’s Rotation: Slowing Down or Speeding Up?

Tags:
- Earth
Earth’s rotation has been slowing down gradually over millions of years, though the change is so small it can’t be noticed in daily life. Billions of years ago, a day on Earth lasted only about 6 hours. Coming forward, during the Jurassic period it was believed to last for about 19 hours as compared to today’s 24 hours.
But recent reports suggest that it has started spinning faster and scientists have no clue why is this happening. However, we have few answers of how Earth can speed up or slow down its rotation? But we’ll tell you some of the most possible reason of how it’s rotation can slow down or speed up? And is it possible that it happens due to human intervention and anything we humans as the protector of the Earth can do?
Let’s see them one by one.
Factors That Can Increase Earth’s Rotation Speed
In the short term, Earth’s rotation can actually speed up slightly because of temporary factors like Earthquakes, shifting air masses, melting glaciers or ocean currents.
How Earthquakes Affect Earth’s Rotation Speed
As we know Earth is made up of various plates known as Tectonic planets. When these Tectonic plates collide with each other we experience Earthquake. One of the well known natural disaster. But how it can speed up earth’s rotation?
High-Magnitude Earthquakes can shift huge masses of rock (plates) inside the Earth, which usually changes its shape slightly. If an earthquake pushes mass closer to the Earth’s axis, the planet spins faster (days become slightly shorter).
Impact of Shifting Air Masses on Earth’s Spin
Life on Earth is possible because of Earth’s atmosphere. We know that our atmosphere contains enormous mass of moving air.
If strong winds push more air toward the poles (closer to axis), Earth can spin slightly faster.
Melting Glaciers and Changes in Earth’s Rotation
Moving ice is called glaciers. These glaciers store water as solid ice. Most of the biggest glaciers of the world (Antartic Circle and Actic Circle) are away from the equator. Due to global warming, glaciers are melting which is very well-known to everyone. As they are melting, the water flows into oceans and mass is being distributed toward lower altitudes. This is redistributing mass across the planet, a process that reminds us how even rogue planets without stars face extreme environmental challenges.
How Melting Glaciers Affect Earth’s Rotation
Glaciers store water as solid ice, often far from the equator. When they melt due to warming, the water flows into oceans, redistributing mass. This typically moves water away from the poles toward lower latitudes, which are farther from the axis. That increases Earth’s moment of inertia, so rotation slows down and days get fractionally longer.
Factors That Can Slow Down Earth’s Rotation Speed
Let’s see the possible reasons of how Earth can spin slower:-
Tidal Friction and Its Effect on Earth’s Rotation
One of the main causes for slowing down of Earth’s rotation is tidal friction which is being created by the gravitational pull between the Earth and the Moon. You must have read in school days that it is the Moon’s gravity which attracts the Ocean water and produces tidal bulges.
These bulges are slightly ahead of the Moon’s position due to Earth’s spin, causing a transfer of rotational energy from Earth to the Moon. As a result, Earth’s rotation slows, and the Moon moves away at about 3.8 centimeters per year.
This gravitational relationship is not unique to Earth; even in the depths of space, interactions like those in Binary Black Hole Habitable Zones: A New Frontier for Life? show how orbital dynamics and energy transfer can shape entire cosmic environments.
Geological Evidence of Earth’s Slowing Spin
Ancient corals, rock formations, and sediment layers act as natural timekeepers, revealing that hundreds of millions of years ago, there were more days in a year because each day was shorter. These geological records match modern scientific predictions. Hence, we can say that Earth is slowing down and it’ll take more time to complete one rotation.
On a much larger scale, the universe itself preserves its history through vast structures like Cosmic Filaments – The Universe’s Astonishing Neural Network, which act as cosmic timekeepers mapping the evolution of galaxies across billions of years.
Modern Measurements of Earth’s Rotation Speed
With atomic clocks and satellite tracking, scientists confirm that Earth’s rotation still changes slightly today. Short-term variations can occur due to earthquakes, melting ice, or shifts in atmospheric mass, which can speed up or slow down the rotation by mere milliseconds and these minute changes are merely noticed by anyone and affects any of our scientific instruments.
Conclusion: Is Earth’s Rotation Slowing or Speeding Up?
Long-Term Trend (Millions of Years)
- Overall Pattern: Slowing down.
- Cause: Tidal friction from the Moon’s gravity.
- Effect: Days are gradually getting longer.
Short-Term Fluctuations (Days to Years)
- Pattern: Sometimes speeding up, sometimes slowing down.
- Causes: Earthquakes, shifting air masses, melting glaciers, ocean currents.
- Effect: Changes are extremely small — usually just a few milliseconds.
What Lies Ahead for Earth’s Spin
In the distant future, Earth’s days will become noticeably longer, but it will take millions of years for any significant difference. For now, Earth’s spin is still slowing overall, though only the most precise scientific instruments can detect these subtle effects.
Frequently Asked Questions About Earth’s Rotation
- Will Earth ever stop spinning?
- Not in any foreseeable future. Earth’s rotation is slowing very gradually due to tidal friction, but it would take billions of years and major planetary changes for it to stop entirely.
- Can humans affect Earth’s rotation?
- Any human influence is negligible. Large human activities redistribute tiny amounts of mass, but only massive geophysical events (like big earthquakes or melting ice on a global scale) can produce measurable, millisecond-level changes in Earth’s rotation speed.
- Has Earth’s rotation recently sped up?
- Short-term speedups do happen and are tracked by scientists. Events such as strong earthquakes, shifts in atmospheric mass, or changes in water distribution can make days fractionally shorter for short periods.
- How much does Earth’s day length change?
- Changes are extremely small: modern variations are typically measured in milliseconds. Over millions of years, tidal friction has lengthened a day by many hours compared to the early Earth.
- How do earthquakes change Earth’s rotation?
- Large, high-magnitude earthquakes can shift mass closer to or farther from Earth’s axis, which slightly alters the planet’s moment of inertia and can speed up or slow down rotation by a few microseconds to milliseconds.
- What is tidal friction and how does it slow Earth’s rotation?
- Tidal friction arises from gravitational interactions with the Moon that create ocean bulges. These bulges transfer angular momentum to the Moon, causing Earth’s rotation to lose a tiny amount of speed while the Moon drifts away.
- Can melting glaciers affect Earth’s rotation?
- Yes. When polar ice melts and water redistributes toward lower latitudes, Earth’s moment of inertia increases and rotation slows slightly. These effects are small but detectable with precise instruments.
- Will day length change noticeably in my lifetime?
- No. Any long-term, noticeable lengthening of the day requires millions of years. Over human lifetimes, changes are tiny and only measurable with atomic clocks and satellite systems.
Comments
Please log in to leave a comment.
Related Posts
Laniakea Supercluster: Our True Cosmic Home
The Laniakea Supercluster is a vast cosmic structure containing our Milky Way and over 100,000 galaxies. Defined by motion, not borders, it reveals our true place in the universe and reshapes how we understand cosmic structure.
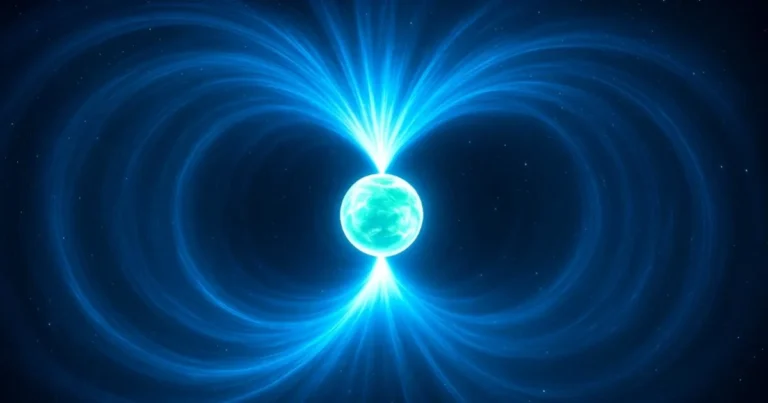

Magnetar: The Universe’s Most Extreme Magnetic Monster
Magnetars are ultra-magnetic neutron stars, cosmic beasts that emit bursts of radiation so powerful they can shake entire galaxies. Learn how they form, what makes them unique, and why their mystery continues to fascinate astronomers.

What Is a Black Hole Shadow? The Ultimate Glimpse into the Abyss
If you could stare into the heart of a galaxy, past the light, past the stars, and into pure darkness, what would you actually see? When astronomers talk about the black hole shadow, they’re referring to one of the most mind-bending sights in the universe, the silhouette of the unseeable, the faint outline of where […]